The biosphere refers to the part of the Earth and its atmosphere where life exists. It includes all living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest animals and plants, as well as the physical environment in which they live and interact.
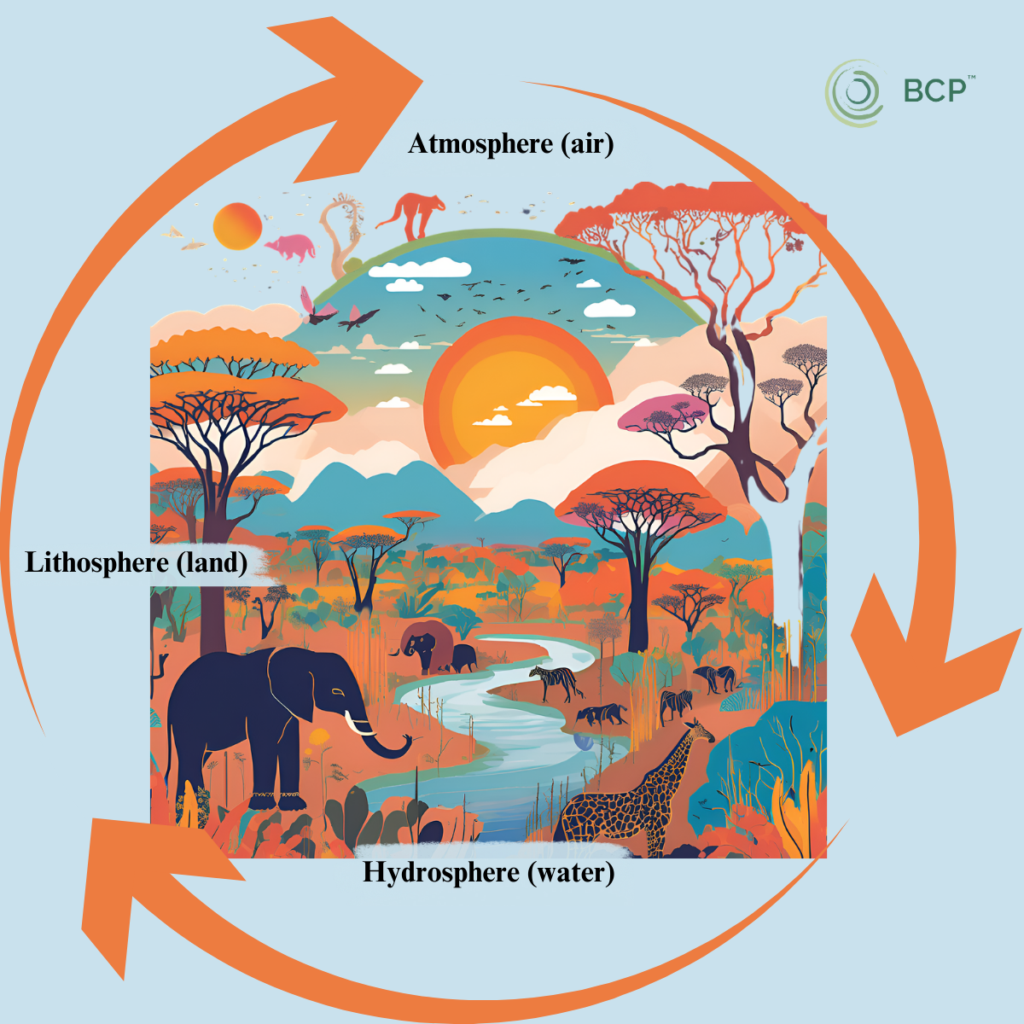
The biosphere is a complex and interconnected system, with living organisms and their environment constantly interacting and influencing each other. For example, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen through photosynthesis, while animals breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Microorganisms play important roles in nutrient cycling and decomposition, while larger animals can act as predators or prey.
Human activities, such as pollution, deforestation, climate change, and others, significantly impact the biosphere. Understanding and protecting the biosphere is important for maintaining the health and well-being of humans and other living organisms.
The biosphere is also closely interconnected with other Earth systems, such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere. The atmosphere provides the oxygen and other gases that living organisms need to survive, while the hydrosphere offers water for drinking and other purposes. The geosphere provides nutrients and minerals that support the growth of plants and other living organisms.

Biodiversity, or the variety of living organisms in the biosphere, is vital for maintaining ecosystem health and functioning. Loss of biodiversity can have significant ecological and economic impacts, such as reduced crop yields, increased susceptibility to disease, and loss of ecosystem services.
One of the key challenges facing the biosphere today is climate change. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and other effects of climate change can significantly impact the distribution and abundance of different species and the functioning of ecosystems. Climate change is also linked to other environmental problems, such as habitat loss and pollution, which can further exacerbate the impacts on the biosphere.
Protecting the biosphere requires a combination of strategies, including conservation of natural habitats and biodiversity, sustainable use of natural resources, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Scientific research, public education, and policy initiatives are important for raising awareness and promoting action to protect the biosphere.

